1.3 背包、队列和栈
1.3.1 API
1.3.1.4 背包
不支持从中删除元素的集合数据类型——它的目的就是帮助用例收集元素并迭代遍历所有收集到的元素
1.3.1.5 先进先出队列
先进先出队列 (或简称队列 )是一种基于先进先出 (FIFO)策略的集合类型
在应用程序中使用队列的主要原因是在用集合保存元素的同时保存它们的相对顺序
1.3.1.6 下压栈
下压栈 (或简称栈 )是一种基于后进先出 (LIFO)策略的集合类型
在应用程序中使用栈迭代器的一个典型原因是在用集合保存元素的同时颠倒它们的相对顺序
1.3.3 链表
链表是一种递归的数据结构,它或者为空(null ),或者是指向一个结点 (node)的引用,该结点含有一个泛型的元素和一个指向另一条
链表的引用。
1.3.3.1 结点记录
1
2
3
4
5
| private class Node
{
Item item;
Node next;
}
|
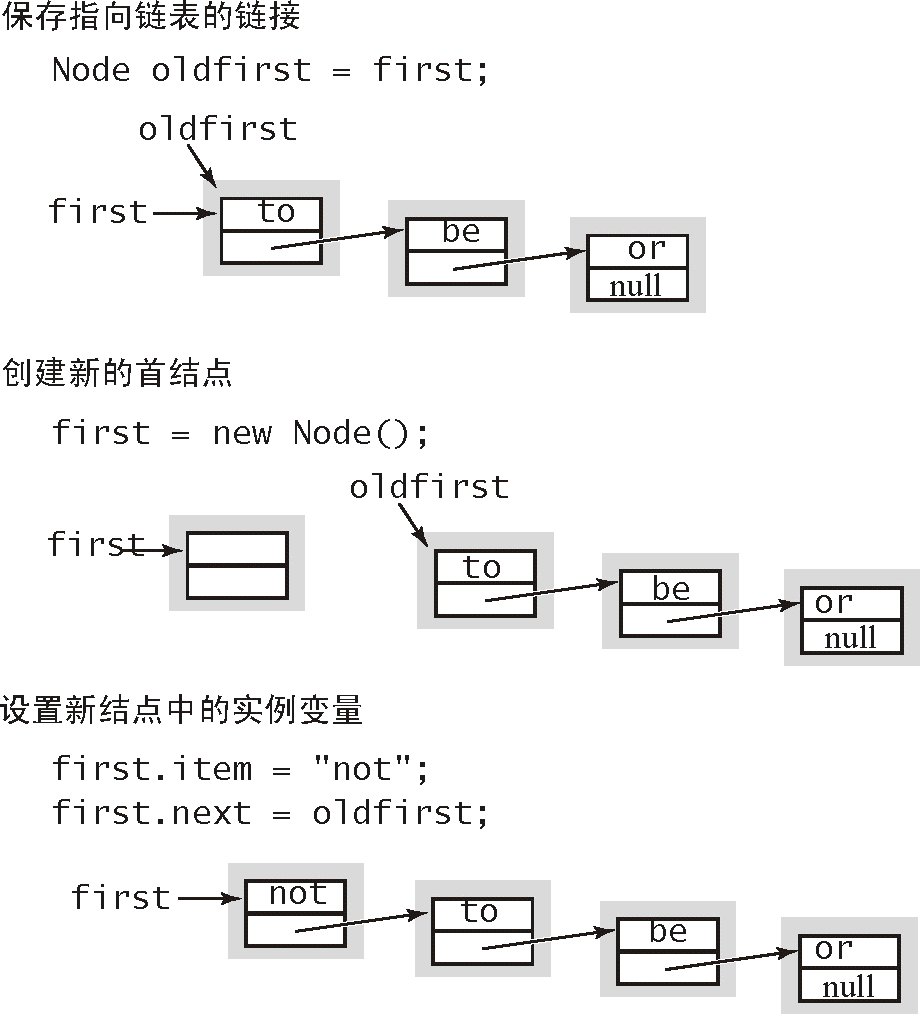
1.3.3.3 在表头插入结点
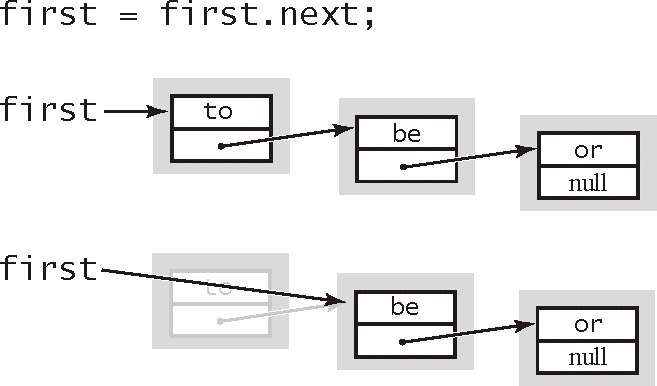
1.3.3.4 从表头删除结点
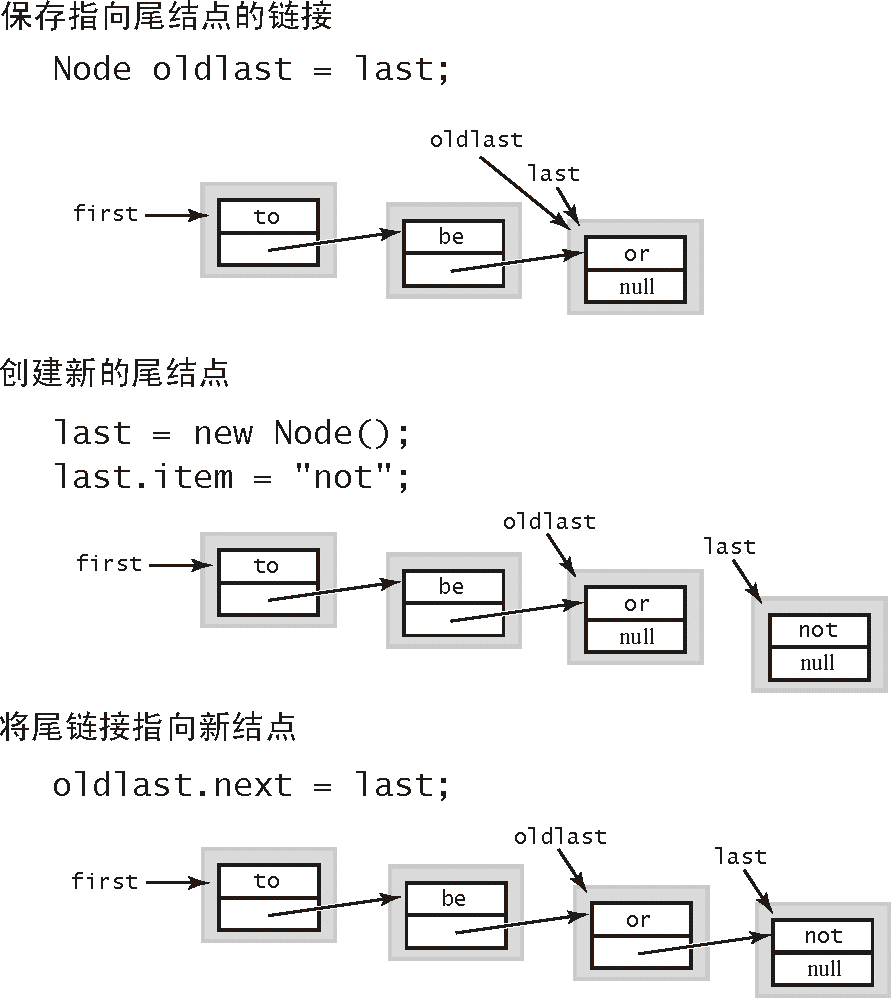
1.3.3.5 在表尾插入结点
1.3.3.6 其他位置的插入和删除操作
实现任意插入和删除操作的标准解决方案是使用双向链表 ,其中每个结点都含有两个链接,分别指向不同的方向
1.3.3.7 遍历
1
2
3
4
| for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next)
{
// 处理x.item
}
|
1.3.3.8 栈的实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| public class Stack<Item> implements Iterable<Item> {
private Node first;//栈顶(最近添加的元素)
private int n;//元素数量
private class Node {
Item item;
Node next;
}
public boolean isEmpty() { return n == 0; }
public int size() { return n; }
public void push(Item item) {
Node oldFirst = first;
first = new Node();
first.item = item;
first.next = oldFirst;
n++;
}
public Item pop() {
Item item = first.item;
first = first.next;
n--;
return item;
}
private class ListIterator implements Iterator<Item> {
private Node current = first;
@Override
public boolean hasNext() { return current != null; }
@Override
public Item next() {
Item item = current.item;
current = current.next;
return item;
}
}
@Override
public Iterator<Item> iterator() { return new ListIterator(); }
}
|
1.3.3.9 队列的实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| public class Queue<Item> {
private Node first;//指向最早添加的节点的链接
private Node last;//指向最近添加的节点的链接
private int n;
private class Node{
Item item;
Node next;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){return n==0;}
public int size(){return n;}
public void enQueue(Item item){
Node oldLast = last;
last = new Node();
last.item = item;
if (isEmpty())first = last;//链表为空时将first和last都指向新结点
else oldLast.next = last;
n++;
}
public Item deQueue(){
Item item = first.item;
first = first.next;
if (isEmpty())last=null;//链表为空时更新last的值
n--;
return item;
}
}
|
1.5 案例研究:union-find 算法
1.5.1 动态连通性
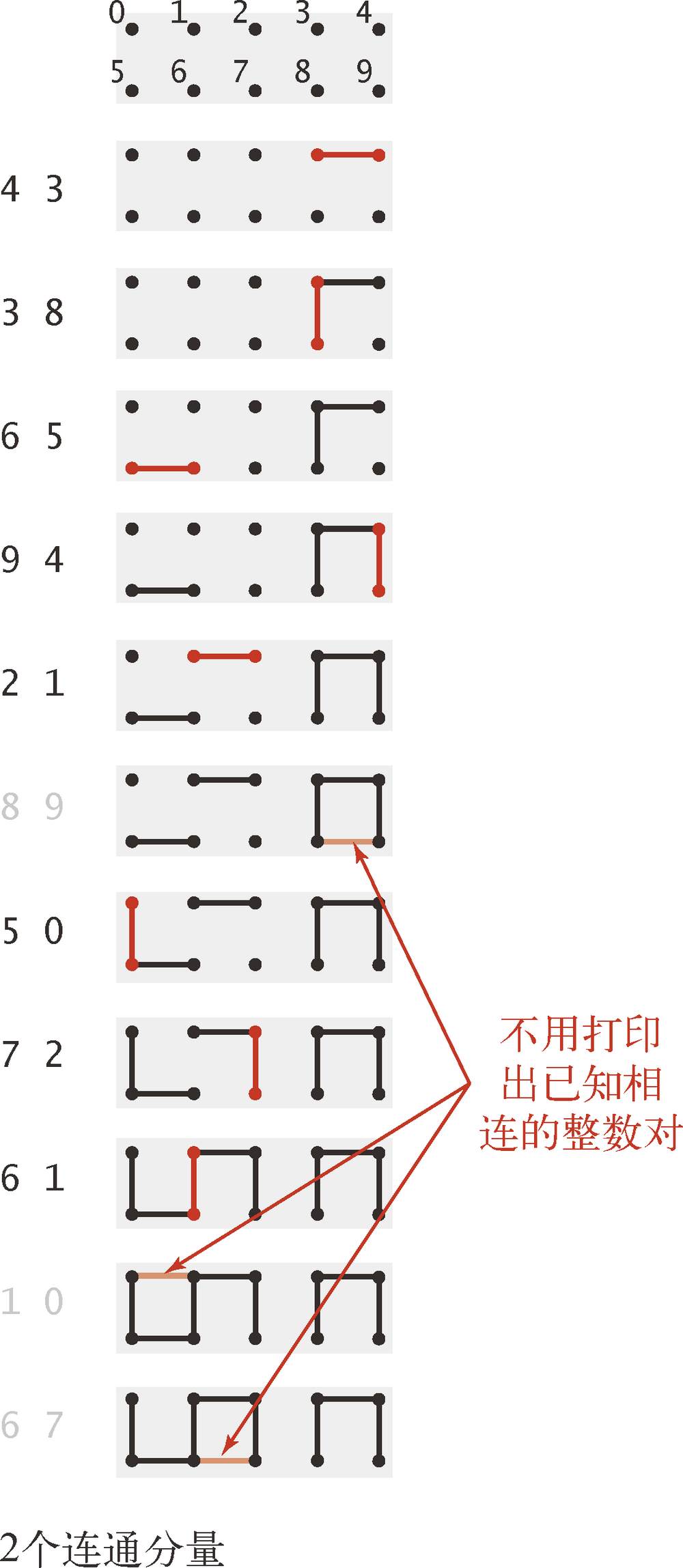
1.5.1.3 数学集合
将对象称为触点,将整数对称为连接,将等价类称为连通分量或是简称分量
| public class UF | |
|---|
| UF(int N) | 以整数标识(0到N-1)初始化N个触点 |
| void union(int p, int q) | 在p和q之间添加一条连接 |
| int find(int p) | p(0到N-1)所在的分量的标识符 |
| boolean connected(int p, int q) | 如果p和q存在于同一个分量中则返回true |
| int count() | 连通分量的数量 |
1.5.2 实现
1.5.2.1 quick-find 算法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| public int find(int p){ return id[p]; }
public void union(int p, int q)
{ // 将p和q归并到相同的分量中
int pID = find(p);
int qID = find(q);
// 如果p和q已经在相同的分量之中则不需要采取任何行动
if (pID == qID) return;
// 将p的分量重命名为q的名称
for (int i = 0; i < id.length; i++)
if (id[i] == pID) id[i] = qID;
count--;
}
|
1.5.2.3 quick-union 算法
每个触点所对应的id[]元素都是同一个分量中的另一个触点的名称(也可能是它自己)——我们将这种联系称为链接。在实现find()方法时,我们从给定的触点开始,由它的链接得到另一个触点,再由这个触点的链接到达第三个触点,如此继续跟随着链接直到到达一个根触点,即链接指向自己的触点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| private int find(int p)
{ // 找出分量的名称
while (p != id[p]) p = id[p];
return p;
}
public void union(int p, int q)
{ // 将p和q的根节点统一
int pRoot = find(p);
int qRoot = find(q);
if (pRoot == qRoot) return;
id[pRoot] = qRoot;
count--;
}
|
1.5.2.8 最优算法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| public class WeightedQuickUnionPathCompressionUF {
private int[] parent;//父链接数组(由触点索引)
private int[] size;//各个根节点所对应的分量的大小
private int count;
public WeightedQuickUnionPathCompressionUF(int n) {
count = n;parent = new int[n];size = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { parent[i] = i;size[i] = 1; }
}
public int find(int p) {
int root = p;
//跟随链接找到根节点
while (root != parent[root]) root = parent[root];
//将在路径上遇到的所有节点都直接链接到根节点
while (p != root) {
int newp = parent[p];
parent[p] = root;
p = newp;
}
return p;
}
public void union(int p, int q) {
int rootP = find(p);
int rootQ = find(q);
if (rootP == rootQ) return;
//将小树的根节点连接到大树的根节点
if (size[rootP] < size[rootQ]) { parent[rootP] = rootQ;size[rootQ] += size[rootP]; }
else { parent[rootQ] = rootP;size[rootP] += size[rootQ]; }
count--;
}
}
|
文章作者
lim
上次更新
2026-01-07
(589ac56)
许可协议
CC BY-NC-ND 4.0




