4.1 无向图
图是由一组顶点和一组能够将两个顶点相连的边组成的
4.1.2 表示无向图的数据类型
| public class Graph | |
|---|
| Graph(int V) | 创建一个含有V个顶点但不含有边的图 |
| Graph(In in) | 从标准输入流 in 读入一幅图 |
| int V() | 顶点数 |
| int E() | 边数 |
| void addEdge(int v, int w) | 向图中添加一条边 v-w |
| Iterable adj(int v) | 和 v 相邻的所有顶点 |
| String toString() | 对象的字符串表示 |
4.1.2.1 图的几种表示方法
邻接表数组:以顶点为索引的列表数组,其中的每个元素都是和该顶点相邻的顶点列表
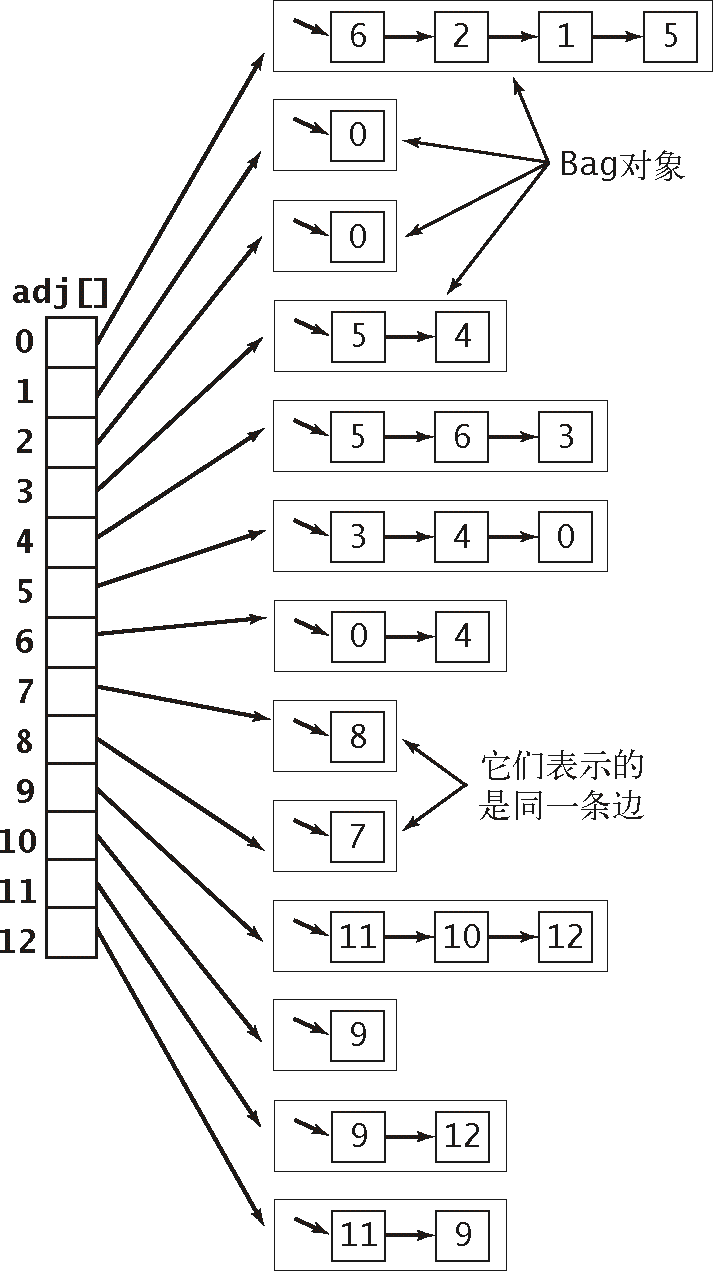
4.1.2.2 邻接表的数据结构
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| public class Graph
{
private final int V; // 顶点数目
private int E; // 边的数目
private Bag<Integer>[] adj; // 邻接表
public Graph(int V)
{
this.V = V; this.E = 0;
adj = (Bag<Integer>[]) new Bag[V]; // 创建邻接表
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) // 将所有链表初始化为空
adj[v] = new Bag<Integer>();
}
public Graph(In in)
{
this(in.readInt()); // 读取V并将图初始化
int E = in.readInt(); // 读取E
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++)
{ // 添加一条边
int v = in.readInt(); // 读取一个顶点
int w = in.readInt(); // 读取另一个顶点
addEdge(v, w); // 添加一条连接它们的边
}
}
public int V() { return V; }
public int E() { return E; }
public void addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].add(w); // 将w添加到v的链表中
adj[w].add(v); // 将v添加到w的链表中
E++;
}
public Iterable<Integer> adj(int v)
{ return adj[v]; }
}
|
4.1.2.3 图的处理算法的设计模式
| public class Search | |
|---|
| Search(Graph G, int s) | 找到和起点 s 连通的所有顶点 |
| boolean marked(int v) | v 和 s 是连通的吗 |
| int count() | 与 s 连通的顶点总数 |
4.1.3 深度优先搜索(DFS)通道
4.1.3.1 走迷宫
Tremaux 搜索
- 选择一条没有标记过的通道,在你走过的路上铺一条绳子
- 标记所有你第一次路过的路口和通道
- 当来到一个标记过的路口时(用绳子)回退到上个路口
- 当回退到的路口已没有可走的通道时继续回退
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| public class DepthFirstSearch
{
private boolean[] marked;
private int count;
public DepthFirstSearch(Graph G, int s)
{
marked = new boolean[G.V()];
dfs(G, s);
}
private void dfs(Graph G, int v)
{
marked[v] = true;
count++;
for (int w : G.adj(v))
if (!marked[w]) dfs(G, w);
}
public boolean marked(int w)
{ return marked[w]; }
public int count()
{ return count; }
}
|
4.1.3.2 热身
深度优先搜索:在访问其中一个顶点时
- 将它标记为已访问
- 递归地访问它的所有没有被标记过的邻居顶点
4.1.3.5 深度优先搜索的详细轨迹
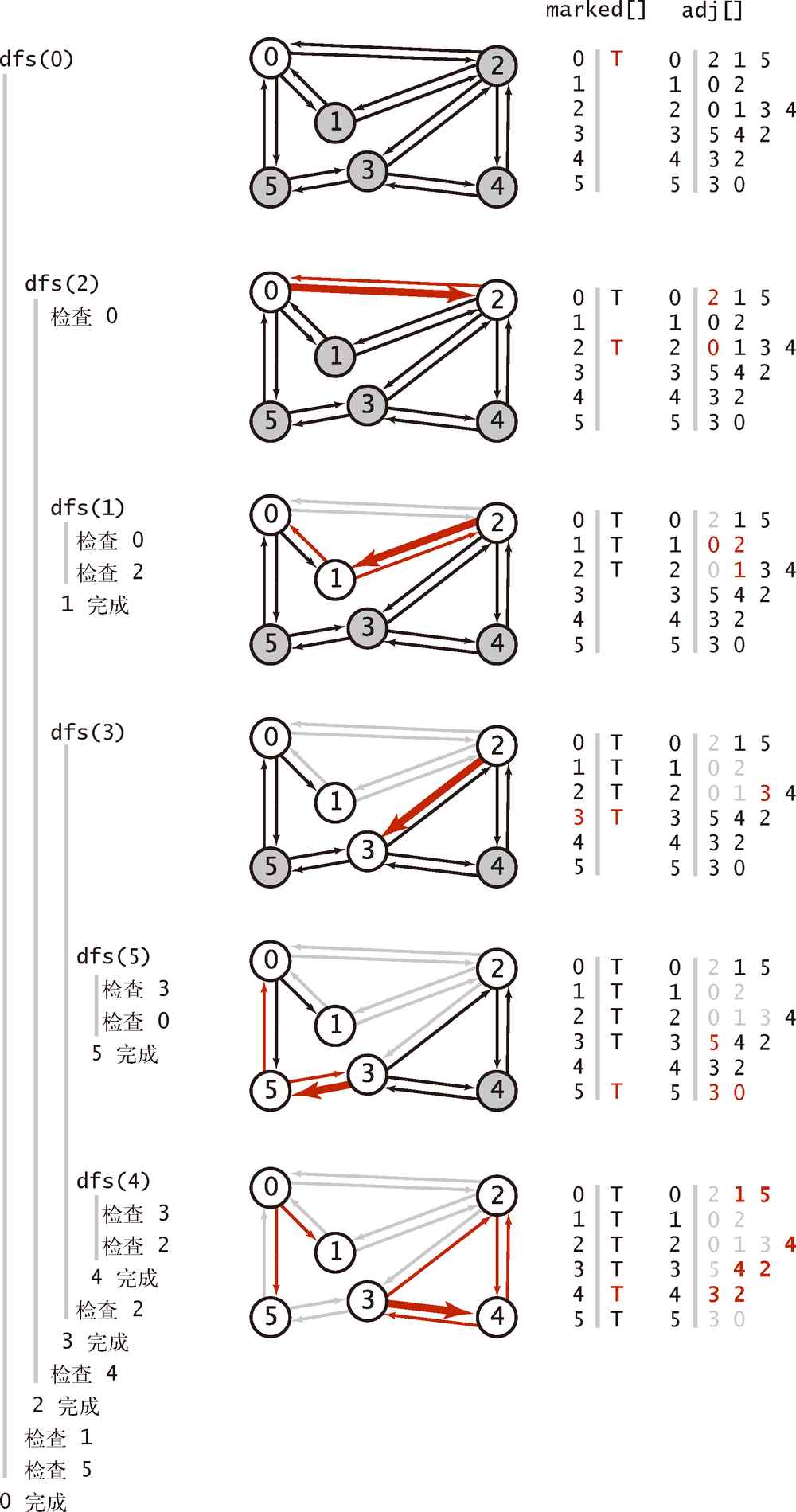
4.1.4 寻找路径
| public class Paths | |
|---|
| Paths(Graph G, int s) | 在 G 中找出所有起点为 s 的路径 |
| boolean hasPathTo(int v) | 是否存在从 s 到 v 的路径 |
| Iterable pathTo(int v) | s 到 v 的路径,如果不存在则返回 null |
4.1.4.1 实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| public class DepthFirstPaths
{
private boolean[] marked; //这个顶点上调用过dfs()了吗?
private int[] edgeTo; //从起点到一个顶点的已知路径上的最后一个顶点
private final int s; //起点
public DepthFirstPaths(Graph G,int s)
{
marked = new boolean[G.V()];
this.s = s;
dfs(G,s);
}
private void dfs(Graph G,int v)
{
marked[v] = true;
for (int w : G.adj(v))
if(!marked[w])
{
edgeTo[w] = v;
dfs(G, w);
}
}
public boolean hasPathTo(int v){return marked[v];}
public Iterable<Integer> pathTo(int v){
if(!hasPathTo(V)) return null;
Stack<Integer> path = new Stack<Integer>();
for(int x = v;x != s;x = edgeTo[x])
path.push(x);
path.push(s);
return path;
}
}
|
4.1.4.2 详细轨迹
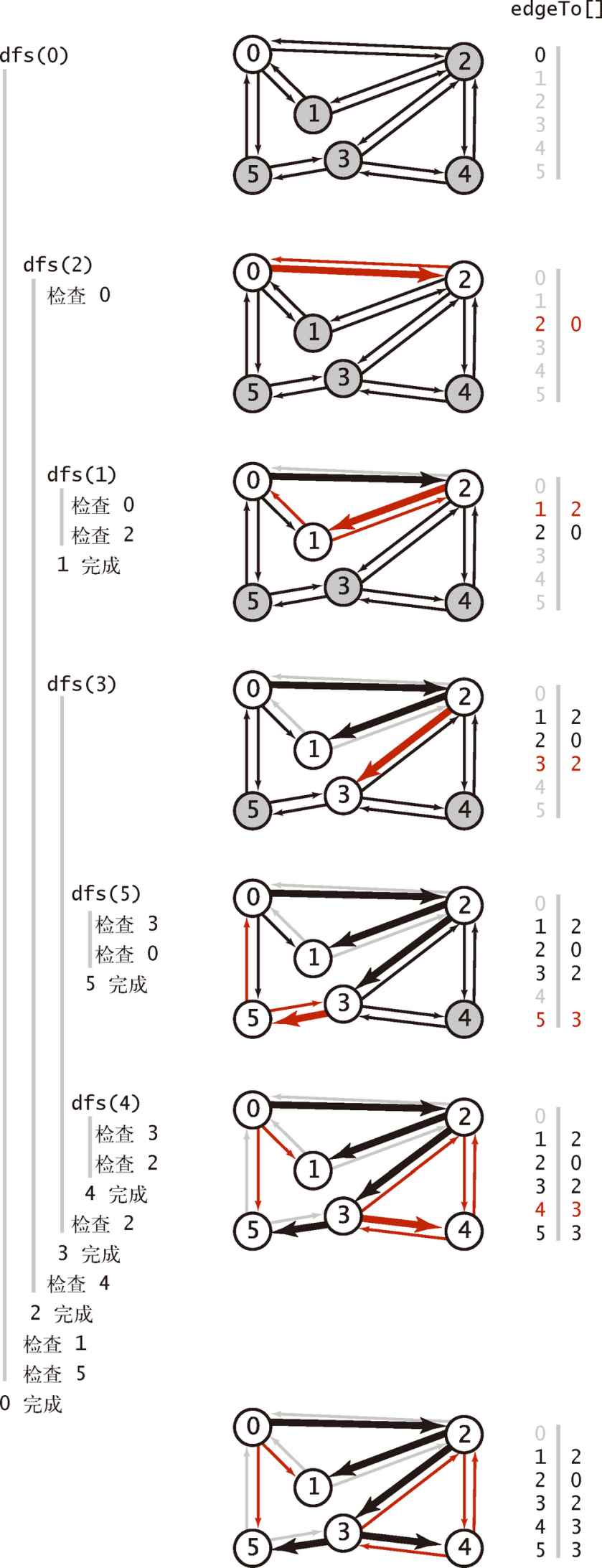
4.1.5 广度优先搜索(BFS)
按照与起点的距离的顺序来遍历所有顶点:使用(FIFO,先进先出)队列
先将起点加入队列,然后重复以下步骤直到队列为空
- 取队列中的下一个顶点 v 并标记它
- 将与 v 相邻的所有未被标记过的顶点加入队列
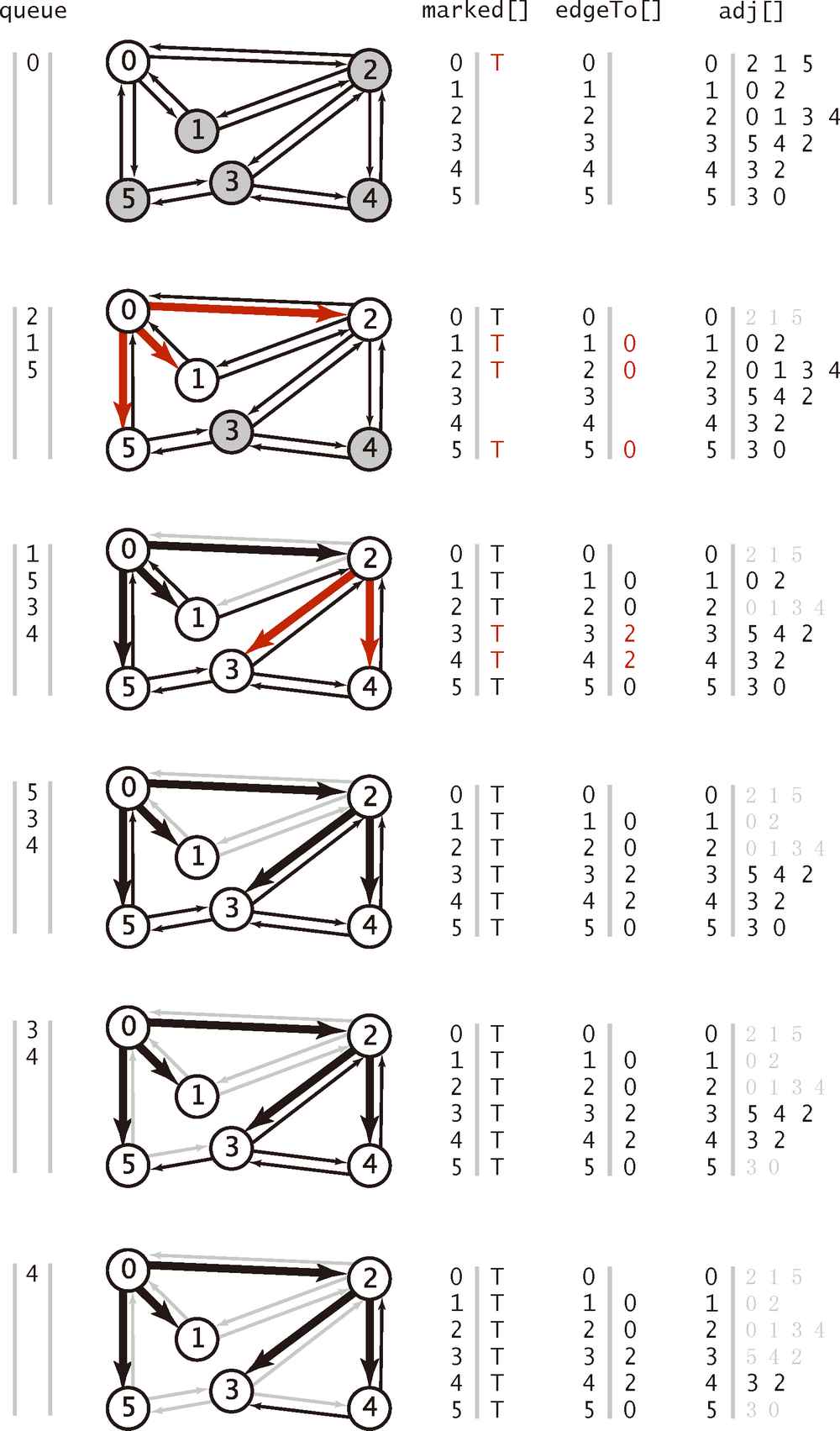
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| public class BreadthFirstPaths
{
private boolean[] marked; // 到达该顶点的最短路径已知吗?
private int[] edgeTo; // 到达该顶点的已知路径上的最后一个顶点
private final int s; // 起点
public BreadthFirstPaths(Graph G, int s)
{
marked = new boolean[G.V()];
edgeTo = new int[G.V()];
this.s = s;
bfs(G, s);
}
private void bfs(Graph G, int s)
{
Queue<Integer> queue = new Queue<Integer>();
marked[s] = true; // 标记起点
queue.enqueue(s); // 将它加入队列
while (!queue.isEmpty())
{
int v = queue.dequeue(); // 从队列中删去下一顶点
for (int w : G.adj(v))
if (!marked[w]) // 对于每个未被标记的相邻顶点
{
edgeTo[w] = v; // 保存最短路径的最后一条边
marked[w] = true; // 标记它,因为最短路径已知
queue.enqueue(w); // 并将它添加到队列中
}
}
}
public boolean hasPathTo(int v)
{ return marked[v]; }
public Iterable<Integer> pathTo(int v)
}
|
4.1.6 连通分量
| public class CC | |
|---|
| CC(Graph G) | 预处理构造函数 |
| boolean connected(int v, int w) | v 和 w 连通吗 |
| int count() | 连通分量数 |
| int id(int v) | v 所在的连通分量的标识符( 0 ~ count()-1 ) |
4.1.6.1 实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| public class CC
{
private boolean[] marked;
private int[] id;
private int count;
public CC(Graph G)
{
marked = new boolean[G.V()];
id = new int[G.V()];
for(int s = 0; s < G.v(); s++)
if(!marked[s])
{
dfs(G, s);
count++;
}
}
private void dfs(Graph G, int v)
{
marked[v] = true;
id[v] = count;
for (int w : G.adj(v))
if(!marked[w])
dfs(G, w);
}
public boolean connected(int v, int w){return id[v] == id[w];}
public int id(int v){return id[v];}
public int count(){return count;}
}
|
文章作者
lim
上次更新
2025-10-25
(a5cc920)
许可协议
CC BY-NC-ND 4.0




